Content
- The Failure of Expensing and Other Depreciation Tax Breaks
- Advantages & Disadvantages of Straight-Line Depreciation
- Property can be placed in service any time during year
- The double declining method of depreciation
- Act before 2014 to claim bonus depreciation or enhanced expensing
- What is a Characteristic of a Fixed Asset?
You can either depreciate or expense these costs when you prepare your tax return. On the other hand, it is possible that JCT and CBO somewhat overstate the revenue impacts. The next sections of this report explain that these provisions may not change business decisions but are claimed for investments that would have been made even in the absence of any such provisions. That would mean they have a significant revenue cost, but little https://online-accounting.net/ or no effect on the economy. If JCT and CBO assumed that the amount of investment eligible for accelerated depreciation would increase significantly in response to these policies, they may have concluded that the revenue impacts were larger than is warranted. The entire theory behind accelerated deprecation provisions starts with the notion that corporate managers respond to these provisions in making their investment decisions.
- Excepted property includes certain intangible property, certain term interests, equipment used to build capital improvements, and property placed in service and disposed of in the same year.
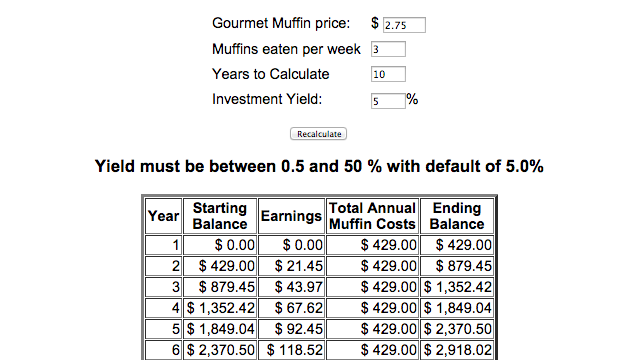
- To calculate the bonus depreciation, you need to multiply the bonus depreciation rate with the cost of the business asset.
- Business expenses are the costs of carrying on a trade or business, and they are usually deductible if the business is operated to make a profit.
- The ability to capitalize on these direct and indirect vehicle and fleet expenses can mean large savings at tax time.
- But in most years, improvements to the restaurant building cannot be expensed.
- Raymond's recapture amount would be computed as shown in the chart that follows.
The Pennsylvania Department of Revenue does not follow the federal tax benefit rule. For tax benefit rules, Pennsylvania law requires depreciation to be computed under the straight-line method even if the depreciation did not provide any tax benefit. If a Depreciation vs Expensing Purchases on Income Taxes taxpayer does not utilize the loss from the PA-40 Schedules C or F, then the assets of the business must be depreciated using straight-line depreciation. Contributions by partners or made on behalf of partners to their retirement plans are not deductible.
The Failure of Expensing and Other Depreciation Tax Breaks
This is done for a few reasons, but the two most important reasons are that the company can claim higher depreciation deductions on their taxes, and it stretches the difference between revenue and liabilities. Depreciation expense is the amount that a company's assets are depreciated for a single period (e.g, quarter or the year), while accumulated depreciation is the total amount of wear to date. The basic difference between depreciation expense and accumulated depreciation lies in the fact that one appears as an expense on the income statement , and the other is a contra asset reported on the balance sheet . However, both pertain to the "wearing out" of equipment, machinery, or another asset. This is because in determining the taxable income limit of such taxpayers, all wages and income are included - even those from another job or separate business activity. Married business owners filing joint returns can also count their spouses' wages and business income. For 2010 through 2013, the annual investment limitation is triggered if the cost of qualified property purchased and placed in service by a business exceeds $2 million.
The above article is intended to provide generalized financial information designed to educate a broad segment of the public; it does not give personalized tax, investment, legal, or other business and professional advice. Before taking any action, you should always seek the assistance of a professional who knows your particular situation for advice on taxes, your investments, the law, or any other business and professional matters that affect you and/or your business. When you purchase items for your business, you can either deduct the full cost of the expense at once, or you can deduct the cost over multiple years . One-time expenses typically reduce your income by a larger amount than depreciating an asset over multiple years. The Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System depreciation method entails that in the first few years, businesses can depreciate the assets more than in the later years of the asset’s life. The special depreciation allowance is 100% for qualified property acquired and placed in service after September 27, 2017 and before January 1, 2023.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Straight-Line Depreciation
When a business buys property, such as a machine or a factory, it's making a capital investment, which is an asset carried on its balance sheet. Tax-wise, the cost of this investment is written off over time , providing tax relief to the business in more than one accounting period.
Is depreciation deductible for income tax purposes?
Depreciation is an annual income tax deduction that allows you to recover the cost or other basis of certain property over the time you use the property.
This is the main reason businesses bother to use bonus depreciation. This suggests that Congress could eliminate accelerated depreciation by repealing MACRS and requiring all depreciation to be done under ADS. In 2011, JCT concluded that this could raise more than $700 billion over a decade. Treasury Department found that this reform would raise less revenue each decade after enactment, so that the savings in the fourth decade would be just 60 percent of the savings in the first decade. This serves as a warning to lawmakers about just how much of the revenue savings they could use to offset new spending or new tax cuts. But this reform would still raise significant revenue even in the long-term.
Property can be placed in service any time during year
Republicans in Congress have discussed making the expensing provision permanent. Pennsylvania law allows IRC section 179 expenses, in effect on Jan. 1, 1986, up to a maximum of $25,000. The federal limitation does not apply for Pennsylvania personal income tax purposes. Taxpayer may use any acceptable method of depreciation if the federal basis and Pennsylvania personal income tax basis are the same. A taxpayer is required to maintain a consistent position for both federal income tax and Pennsylvania personal income tax purposes. Interest, dividends, rents, and royalty income not derived in the ordinary course of business are not reportable as profits from a business, profession or farm, and expenses, which are attributable to such income, are not deductible business expenses. Only then would the interest and dividends be net taxable as net profits from the operation of a commercial enterprise.

